YOU CAN LIVE TWICE :BE A DONOR..BE A HERO.
YOU CAN LIVE TWICE :Be an Organ Donor.
A. What is organ donation?
Organ donation is the process of Retrieving or Procuring an organ from a live or deceased person known as a DONOR. The process of recovering organs is called HARVESTING. This organ is transplanted into the RECEPIENT who is in need of that organ.
Live Donation is from a healthy and living person. This can only be done in the case of a liver or a kidney (because the liver can grow back to its normal size, and a donor can survive on one kidney). So if a near relative of yours needs a liver or a kidney, anyone in the immediate family can donate to them.
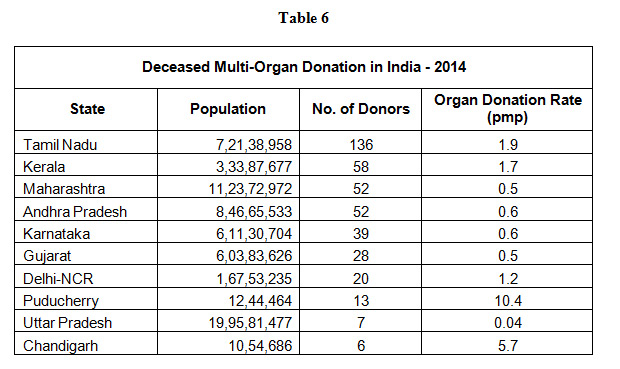
TAMILNADU NUMBER ONE STATE IN ORGAN DONATION IN INDIA---Watch NDTV
B. What is Brain death and how it is related to organ donation?
A brain dead person has absolutely no chance of recovering. Brain death is a form of death and is irreversible. To know more about Brain Death-follow this link and watch the short and easy to understand film on What is Brain Death?
Once Brain Death has been declared, you are dead – BUT – your organs are still alive because they have been kept alive through artificial means.
This means that if a person dies at home or anywhere else, and their heart stops beating, they cannot donate their vital organs. The organs of a person who has died a cardiac death (as opposed to brain death) will die within minutes of the heart stopping.
Therefore – The only time you can donate your vital organs is if you are in hospital and have been declared brain dead.
C. Who can donate?
Almost anyone of nearly any age and average health can donate an organ. Although anyone who has cancer, HIV or disease-causing bacteria in the bloodstream or body tissues is usually exempt from donation, this is not always the rule.
Decisions about an organ’s usability are made at the donor’s time of death or, in the case of living donors, in the process leading to donation.
D. Organ transplantation procedures for brain death – India
According to the provisions of the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, known as THOA, the protocol for declaration of brain death is as follows :
Panel of 4 doctors need to declare the brain death twice in a span of 6 hours. 2 of these doctors must be from a panel approved by the government. This panel includes:
i. Registered Medical Practitioner in charge of the Hospital where brain stem death has occurred.
ii. Registered Medical Practitioner nominated from the panel of names sent by the hospitals and approved by the Appropriate Authority.
iii. Neurologist/Neuro-Surgeon (where Neurologist/Neurosurgeon is not available, any Surgeon or Physician and Anaesthetist or Intensivist,Nominated by Medical Administrator In-charge from the panel of names sent by the hospital and approved by the Appropriate Authority shall be included.
iv. Registered medical practitioner treating the aforesaid deceased person. The same is recorded on Form 10 of the THO Act 2014. The family’s consent is obtained on Form 8.
Healthy organs are transplanted from the body of the patient as soon as possible.
ii. Registered Medical Practitioner nominated from the panel of names sent by the hospitals and approved by the Appropriate Authority.
iii. Neurologist/Neuro-Surgeon (where Neurologist/Neurosurgeon is not available, any Surgeon or Physician and Anaesthetist or Intensivist,Nominated by Medical Administrator In-charge from the panel of names sent by the hospital and approved by the Appropriate Authority shall be included.
iv. Registered medical practitioner treating the aforesaid deceased person. The same is recorded on Form 10 of the THO Act 2014. The family’s consent is obtained on Form 8.
Healthy organs are transplanted from the body of the patient as soon as possible.
i. Heart and lungs are the most sensitive organs, and must be transplanted within four to six hours of retrieval.
ii. Liver and pancreas must be transplanted within 12 hours and kidneys within 24 hours of retrieval.
iii. In the interim, all organs are stored at 4°C (in a special preservative solution stored in an ice-filled chamber) to help with preservation.
No payment is made to the donor family, and the recipient is not charged for the organs per se. They of course have to pay the transplantation costs of the hospital. All billing for the donor family stops from the time that they give consent for organ donation.
ii. Liver and pancreas must be transplanted within 12 hours and kidneys within 24 hours of retrieval.
iii. In the interim, all organs are stored at 4°C (in a special preservative solution stored in an ice-filled chamber) to help with preservation.
No payment is made to the donor family, and the recipient is not charged for the organs per se. They of course have to pay the transplantation costs of the hospital. All billing for the donor family stops from the time that they give consent for organ donation.
E. Which organ can be donated?
Let’s take a closer look at the different organs that can be donated. There are six organs that can be donated and transplanted :
1. Kidney — The functioning lifespan of a transplanted kidney is about nine years. Of all organs, kidneys are most in demand and the most frequently donated. Most diseases that affect the kidneys affect both at the same time, so a living donor is generally not at a greater health risk with only one kidney.
2. Liver — The liver is necessary for vitamin storage, removing waste from blood and digestion. The liver is the only organ that can grow cells in order to regenerate itself. A liver can actually be split in two and transplanted into two different people. A living person can have a portion of the liver removed, and the remaining portion will regenerate to almost its full previous size.
3. Heart — A heart will beat about 2.5 billion times in the course of an average lifetime. Once removed from the donor’s body, a heart can only survive for about four hours.
4. Lungs — Single or double-lung transplants can be performed. Additionally, living donors can donate a single lobe from the lungs, though it will not regenerate.
5. Pancreas — It’s possible to make a living donation of a portion of the pancreas and still retain pancreas functionality.
6. Intestine — Although quite rare, a living donor can donate a portion of the intestine.
2. Liver — The liver is necessary for vitamin storage, removing waste from blood and digestion. The liver is the only organ that can grow cells in order to regenerate itself. A liver can actually be split in two and transplanted into two different people. A living person can have a portion of the liver removed, and the remaining portion will regenerate to almost its full previous size.
3. Heart — A heart will beat about 2.5 billion times in the course of an average lifetime. Once removed from the donor’s body, a heart can only survive for about four hours.
4. Lungs — Single or double-lung transplants can be performed. Additionally, living donors can donate a single lobe from the lungs, though it will not regenerate.
5. Pancreas — It’s possible to make a living donation of a portion of the pancreas and still retain pancreas functionality.
6. Intestine — Although quite rare, a living donor can donate a portion of the intestine.
In addition to organs, you can also donate tissue, blood stem cells, blood and platelets, and even your body.
Tissues : It is composed of layers of cells that function together to serve a specific purpose. It must be donated within 24 hours of death.
Tissues : It is composed of layers of cells that function together to serve a specific purpose. It must be donated within 24 hours of death.
7.Cornea: One of the most commonly transplanted tissues each year is the cornea. It is a transparent covering over the eye — is the eye’s primary focusing component. A cornea transplant restores sight to recipients blinded by an accident, infection or disease. Corneas can be transplanted whole or in parts and require no anti-rejection drugs in the recipient. Corneas from a 75-year-old donor are just as effective as younger corneas.
8.Bones: Donated bones can be used to replace cancerous bones in the arm or leg in lieu of amputation.
8.a . Skin: Among its many uses, skin can be used in grafts for burn victims or for post-mastectomy breast reconstruction.
9.Veins: Donated veins are used in cardiac bypass surgery.
Other donated tissue includes tendons, ligaments, heart valves and cartilage.
- Panel of 4 doctors need to declare the brain death twice in a span of 6 hours. 2 of these doctors must be from a panel approved by the government. This panel includes:
a) Registered Medical Practitioner in charge of the Hospital where brain stem death has occurred.
b) Registered Medical Practitioner nominated from the panel of names sent by the hospitals and approved by the Appropriate Authority.
c) Neurologist/Neuro-Surgeon (where Neurologist/Neurosurgeon is not available, any Surgeon or Physician and Anaesthetist or Intensivist, Nominated by Medical Administrator In-charge from
the panel of names sent by the hospital and approved by the Appropriate Authority shall be included.
d) Registered medical practitioner treating the aforesaid deceased person. The same is recorded on Form 10 of the THO Act 2014.
DISCLAIMER: " The things expressed on this Blog is for informational purpose only. This is my personal blog. All information is provided on an as-is basis. Feel free to challenge me, disagree with me, or tell me I’m completely nuts in the comments section of each blog entry, but I reserve the right to delete any comment for any reason whatsoever (abusive, profane, rude, or anonymous comments)" – Thank you.
























Comments
Post a Comment